RS2875.165 (2.875 in Pipe Section) with 8''-10''-12'' Helixes
A. Project description
This example presents a detailed example for calculating the ultimate axial capacity of a helical pile according to Vesic 1974 and Meyerhoff/Hansen method. Table 1 below presents assumed soil properties, Table 2 summarizes the soil stratigraphy, while Table 3 describes assumed helical pile properties.
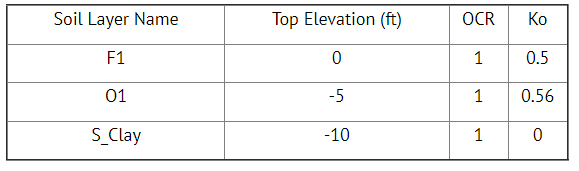
Table 1: Soil properties
Table 2: Stratigraphy (Boreholes)
Table 3: Helical pile properties
Soil Properties and Model in HelixPile
Pile Section Properties and Helix Configuration
B. Ultimate bearing capacity calculations – Cylinder failure method
B1. Manual calculations
For the cylinder lateral pressures factor, we will use the Mitch – Clemence method:
K = 0.09e(0.08fr) = 0.09
Table 4: Ultimate shear stress line force calculations.
Figure: Ultimate shear stress line force on cylinder body.
Cylinder strength: Fcylinder = A1 + A2 = 14375 + 9420 = 23795 lbs = 23.8 kips
Vesic method
Tip: Fult = 0.86 kips (compression)
Plate 1: Fult = 5.85 kips (compression)
Plate 3: Fult = 13.89 kips (tension)
So, the utimate cylinder compression capacity is Fult, comp = 23.8 + 0.86 + 5.85= 30.51 kips
The utimate cylinder tension capacity is Fult, tension = 23.8 + 13.89 = 37.69 kips
Meyerhoff/Hansen
Tip: Fult = 0.81 kips
Plate 1: Fult = 5.58 kips
Plate 3: Fult = 13.32 kips
So, the utimate cylinder compression capacity is Fult, comp = 23.8 + 0.81 + 5.58 = 30.19 kips
The utimate cylinder tension capacity is Fult, tension = 23.8 + 13.32 = 37.12 kips
B2. Calculations with HelixPile
The following images present the calculated compression and tension cylinder capacities with the Vesic and Meyerhoff/Hansen methods respectively. The analysis has been performed with HelixPile software.
Figure: Cylinder Capacities in HelixPile - Vesic Method
Figure: Cylinder Capacities in HelixPile - Meyerhoff/Hansen Method
Table 5: Comparison between manual calculations and HelixPile results.